
Google has addressed a Cloud Platform (GCP) security vulnerability impacting all users and allowing attackers to backdoor their accounts using malicious OAuth applications installed from the Google Marketplace or third-party providers.
Named GhostToken by Astrix Security, the Israeli cybersecurity startup that found and reported it to Google in June 2022, this security flaw was addressed via a global patch that rolled out in early April 2023.
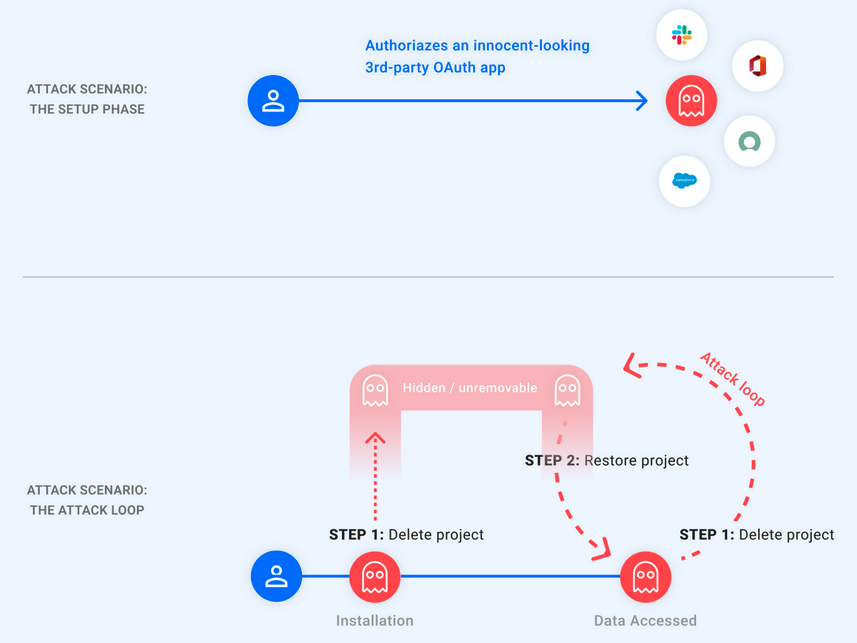
After being authorized and linked to an OAuth token that gives it access to the Google account, malicious apps could be made invisible by attackers after exploiting this vulnerability.
This would hide the app from Google's application management page, the only place where Google users can manage apps connected to their accounts.
"Since this is the only place Google users can see their applications and revoke their access, the exploit makes the malicious app unremovable from the Google account," Astrix Security said.
"The attacker on the other hand, as they please, can unhide their application and use the token to access the victim's account, and then quickly hide the application again to restore its unremovable state. In other words, the attacker holds a 'ghost' token to the victim's account."
To hide malicious apps authorized by the victims, attackers only had to make them enter a 'pending deletion' state by deleting the linked GCP project.
However, after restoring the project, they would be provided with a refresh token that made it possible to retrieve a new access token that could be used to gain access to the victims' data.
These steps could be repeated in a loop, allowing the attackers to delete and restore the GCP project to hide the malicious app each time they needed access to the victim's data.
The attack's impact depends on the permissions granted to the malicious apps installed by the victims.
The vulnerability "allows attackers to gain permanent and unremovable access to a victim's Google account by converting an already authorized third-party application into a malicious trojan app, leaving the victim's personal data exposed forever," Astrix Security Research Group said.
"This may include data stored on victim's Google apps, such as Gmail, Drive, Docs, Photos, and Calendar, or Google Cloud Platform's services (BigQuery, Google Compute, etc.)."
Google's patch allows GCP OAuth applications in 'pending deletion' states to appear on the 'Apps with access to your account' page, allowing users to remove them and protect their accounts from hijack attempts.
Astrix advises all Google users to visit their account's app management page and check all authorized third-party apps, ensuring that each of them has only the permissions they require to function.


Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now