Importance of Internet Security in Educational Environment
The educational landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation in recent years, with technology weaving itself into the very fabric of learning. From interactive online platforms to collaborative digital tools, technology opens doors to a world of possibilities. However, with this increased reliance on the internet comes a heightened sense of vulnerability. Cyber threats lurk in the shadows, posing a significant risk to students, staff, and sensitive data. In this environment, robust internet security measures become more crucial than ever before. The internet has become an integral part of our lives, especially in the educational environment. Schools, colleges, and universities rely heavily on the internet for teaching, learning, research, and administration. However, with the increased use of the internet comes the risk of cyber threats, making internet security a crucial aspect of an educational institution’s IT infrastructure.
Internet security refers to the measures taken to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems on the internet. It involves protecting networks, devices, programs, and data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Importance of Internet Security
The educational sector is a prime target for cyber attackers due to the sensitive data it holds, such as student records, financial information, and intellectual property. A successful cyber-attack can result in significant financial losses, damage to reputation, and disruption of operations.
Here are some reasons why internet security is essential in educational environments:
- Protecting Student and Staff Data
Educational institutions collect and store a vast amount of personal data, including student records, staff information, and financial details. This data is a valuable target for cybercriminals, who can use it for identity theft, fraud, or extortion. Robust internet security measures are necessary to protect this sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse.
- Safeguarding Intellectual Property
Schools, colleges, and universities are centers of research and innovation, generating valuable intellectual property in the form of research papers, patents, and other proprietary information. Cybercriminals may target this information for financial gain or to gain a competitive advantage. Internet security measures can help prevent the theft or unauthorized disclosure of this sensitive data.
- Ensuring Business Continuity
Cyber-attacks can disrupt the normal operations of an educational institution, causing significant financial losses and reputational damage. A successful cyber-attack can lead to system downtime, data loss, or even the complete shutdown of critical systems. Effective internet security measures can help ensure the availability and continuity of critical systems and data, minimizing the impact of cyber threats.
- Compliance with Regulations
Educational institutions are subject to various regulations and laws related to data privacy and security, such as the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) in the United States. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal consequences and financial penalties. Implementing robust internet security measures can help educational institutions comply with these regulations and avoid costly legal battles.
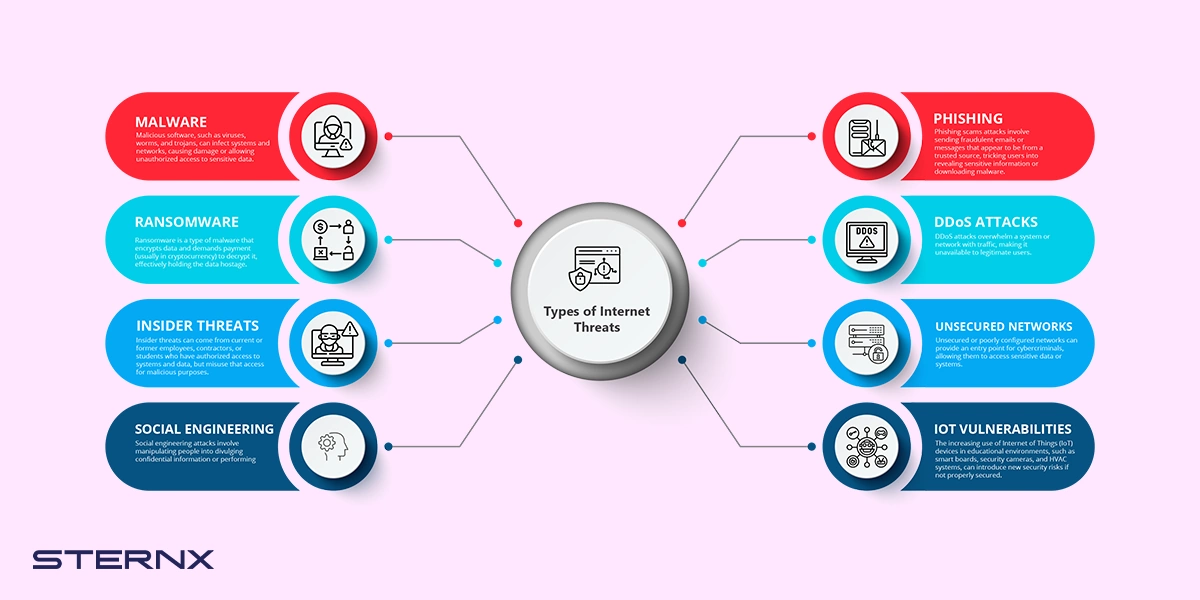
Types of Internet Threats
Educational institutions face a wide range of cyber threats, including:
- Malware: Malicious software, such as viruses, worms, and trojans, can infect systems and networks, causing damage or allowing unauthorized access to sensitive data.
- Phishing: Phishing scams attacks involve sending fraudulent emails or messages that appear to be from a trusted source, tricking users into revealing sensitive information or downloading malware.
- Ransomware: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts data and demands payment (usually in cryptocurrency) to decrypt it, effectively holding the data hostage.
- Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: DDoS attacks overwhelm a system or network with traffic, making it unavailable to legitimate users.
- Insider Threats: Insider threats can come from current or former employees, contractors, or students who have authorized access to systems and data, but misuse that access for malicious purposes.
- Unsecured Networks: Unsecured or poorly configured networks can provide an entry point for cybercriminals, allowing them to access sensitive data or systems.
- Social Engineering: Social engineering attacks involve manipulating people into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
- IoT Vulnerabilities: The increasing use of Internet of Things (IoT) devices in educational environments, such as smart boards, security cameras, and HVAC systems, can introduce new security risks if not properly secured.
Best Practices for Internet Security
To mitigate the risks posed by these threats, educational institutions should implement a comprehensive internet security strategy that includes the following best practices:
- Develop and Enforce a Robust Security Policy: A comprehensive security policy should outline acceptable use of technology resources, password management practices, data handling procedures, and incident response protocols. This policy should be regularly updated and enforced across the institution.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide two-factor authentication (such as a password and a one-time code) to access systems or data. This can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Regularly Update Software and Systems: Keeping software, operating systems, and firmware up-to-date is crucial to addressing known vulnerabilities and patching security flaws. Establish a regular patching schedule and automate updates where possible.
- Use Endpoint Protection and Antivirus Solutions: Endpoint protection and antivirus solutions can detect and prevent malware, ransomware, and other cyber threats from infecting devices and networks. Ensure these solutions are up-to-date and deployed on all endpoints, including servers, workstations, and mobile devices.
- Implement Network Segmentation: Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit the potential impact of a security breach. By separating critical systems and data from less sensitive resources, network segmentation can contain the spread of malware and limit access to sensitive data.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications before they can be exploited by cybercriminals. Engage third-party security experts to perform these assessments and provide recommendations for improving security posture.
- Educate Users on Cyber Security Best Practices: Users are often the weakest link in an organization’s security posture. Educate students, staff, and faculty on cyber security best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts, using strong passwords, and the importance of keeping software and systems up-to-date.
- Implement a Robust Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategy: In the event of a successful cyber attack, a robust backup and disaster recovery strategy can help minimize data loss and system downtime. Regularly backup critical data and systems, and test disaster recovery procedures to ensure they are effective.
- Monitor and Respond to Security Incidents: Real-time monitoring of networks and systems can help detect security incidents as they occur, allowing for a faster response and mitigation of potential damage. Establish an incident response plan that outlines steps for containing and recovering from a security breach.
- Continuously Evaluate and Improve Security Measures: Cyber threats are constantly evolving, and an effective security strategy must adapt to meet these changing risks. Continuously evaluate and improve security measures based on new threats, vulnerabilities, and best practices.
Internet security in schools is a shared responsibility, requiring collaboration between school administrators, educators, students, and parents. By proactively implementing robust security measures, fostering cyber awareness, and promoting responsible online behavior, we can create a safe and secure learning environment where technology empowers, rather than endangers, our future generations. Remember, the journey towards a secure digital security learning space is an ongoing process, requiring continuous vigilance and adaptation. Let’s work together to safeguard the online world for our students and ensure their educational journey is enriched by technology, not compromised by its threats.
In the digital age, internet security is a critical aspect of an educational institution’s IT infrastructure. With the increasing reliance on the internet for teaching, learning, research, and administration, schools, colleges, and universities must implement robust security measures to protect sensitive data, intellectual property, and ensure business continuity.
By developing and enforcing a comprehensive security policy, implementing multi-factor authentication, regularly updating software and systems, using endpoint protection and antivirus solutions, implementing network segmentation, conducting regular security audits and penetration testing, educating users on cyber security best practices, implementing a robust backup and disaster recovery strategy, monitoring and responding to security incidents, and continuously evaluating and improving security measures, educational institutions can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats and ensure a secure online environment for students, staff, and faculties.
The post Importance of Internet Security in Educational Environment appeared first on SternX Technology.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from SternX Technology authored by Ernest Frimpong. Read the original post at: https://sternx.ae/en/internet-security/





