ZingoStealer crimeware released for free in the cybercrime ecosystem
Security Affairs
APRIL 15, 2022
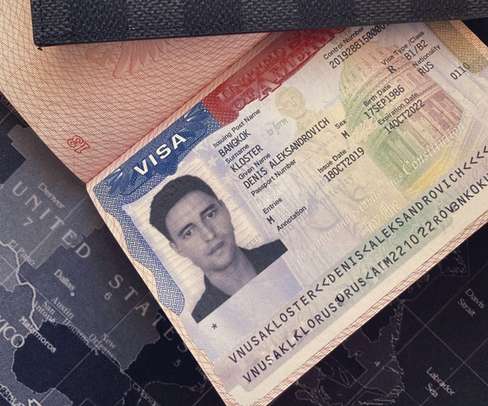
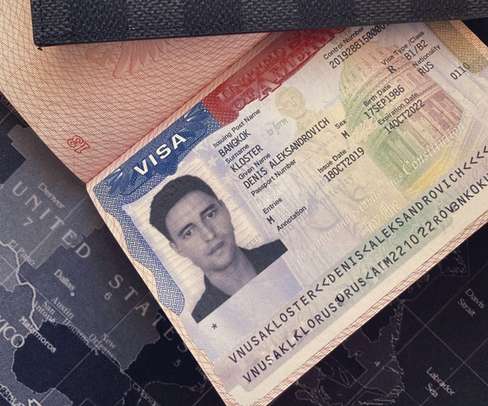
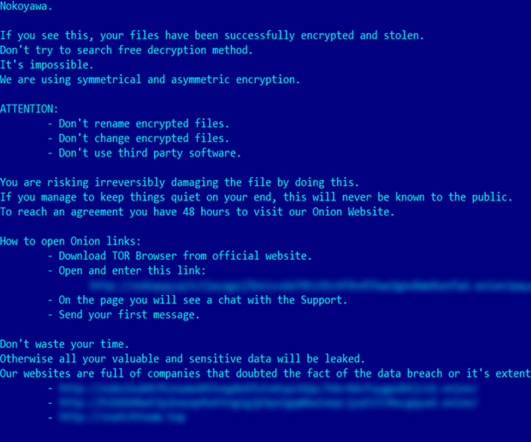
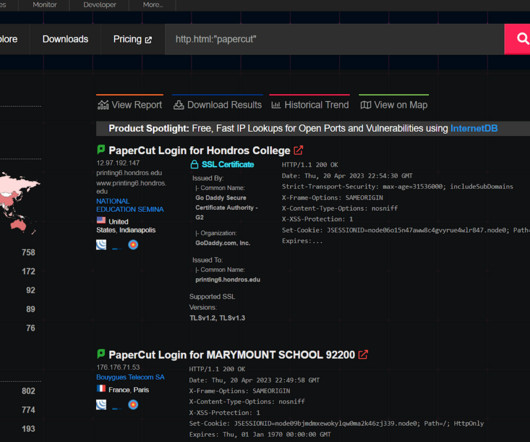
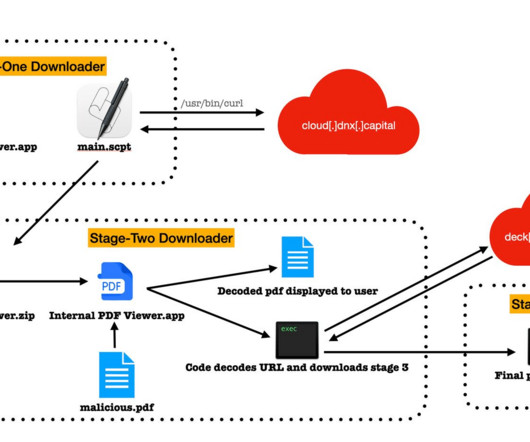
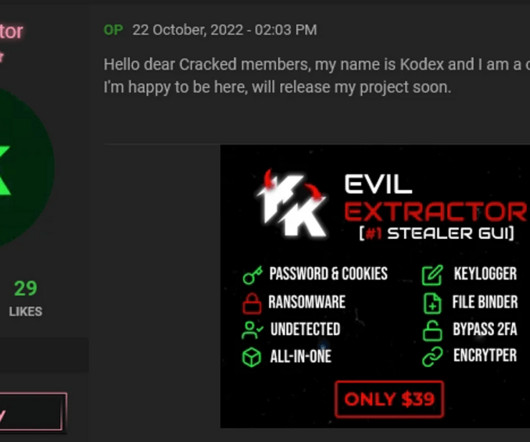
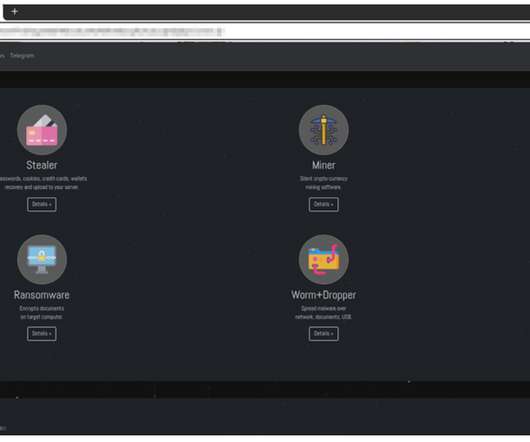
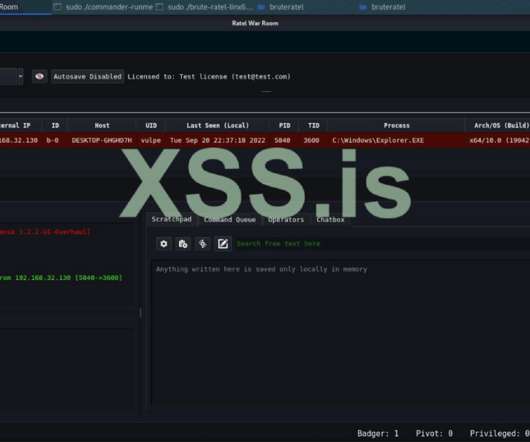
The cybercrime gang has been active since at least January 2020. The malware is also able to steal details from cryptocurrency wallets and load additional malware to conduct malicious operations. “It features the ability to steal sensitive information from victims and can download additional malware to infected systems.

























Let's personalize your content