
A vulnerability in the Peloton Bike+fitness machine has been fixed that could have allowed a threat actor to gain complete control over the device, including its video camera and microphone.
Peloton is the manufacturer of immensely popular fitness machines, including the Peloton Bike, Peloton Bike+, and the Peloton Tread.
In a new report released by McAfee, researchers explain how they purchased a Peloton Bike+ to poke at the underlying Android operating system and see if they could find a way to compromise the device.
"Under the hood of this glossy exterior, however, is a standard Android tablet, and this hi-tech approach to exercise equipment has not gone unnoticed," explains McAfee security researchers Sam Quinn and Mark Bereza.
"Viral marketing mishaps aside, Peloton has garnered attention recently regarding concerns surrounding the privacy and security of its products. So, we decided to take a look for ourselves and purchased a Pelton Bike+."
Android allows devices to boot a modified image using a special command called 'fastboot boot,' which loads a new boot image without flashing the device and enable the device to revert to its default boot software on reboot.
Newer Android versions allow developers to place the device in a locked state to prevent a device from loading modified boot images. As you can see below, the 'fastboot oem device-info' shows that the device is not unlocked.
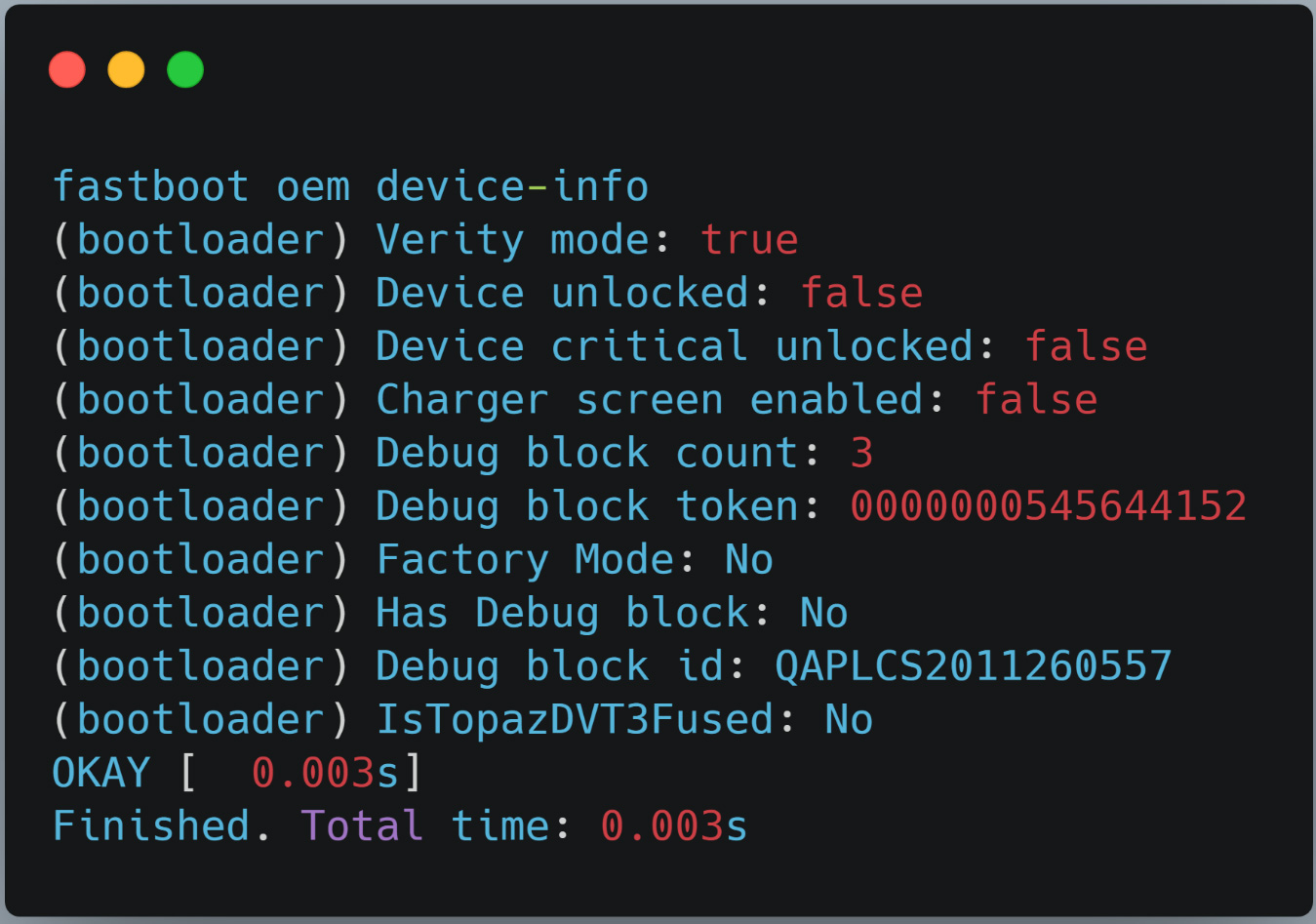
While Peloton correctly set the device to a locked state, McAfee researchers discovered that they could still load a modified image as a bug was preventing the system from not verifying if the device was unlocked.
While their test boot image failed as it did not contain the correct display and hardware drivers to operate the Peloton, it showed that modified code could be run on the device.
The researchers then acquired a valid Peloton boot image from the device's OTA (over-the-air) updates. They then modified the legitimate boot image to include the 'su' command to elevate privileges on the device.
With physical access to the device, the researchers loaded a modified Peloton boot.img into the Peloton Bike+, they were able to achieve root access on the device using the 'su' command, as shown by the image below.
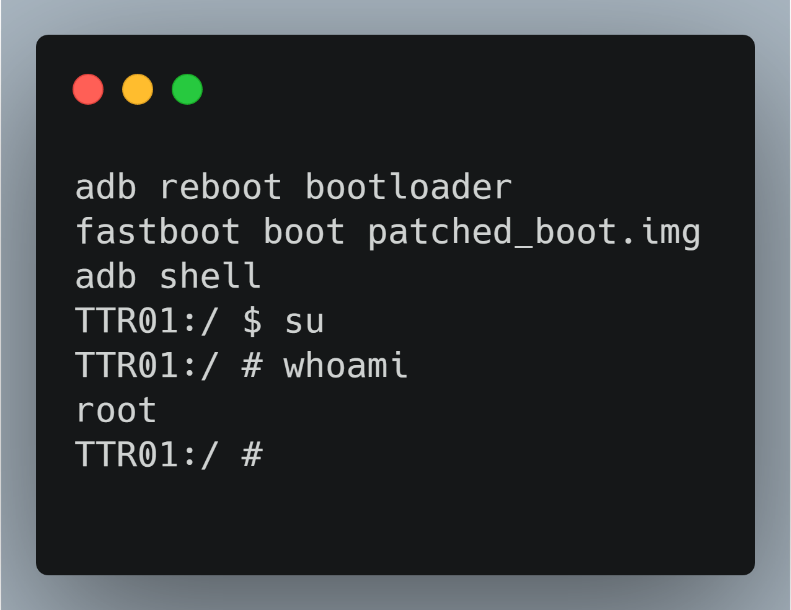
While the Peloton Bike+ continued to operate and look just like usual, the researchers now had elevated access and could run any Android application they wanted on the device.
McAfee said they reported the vulnerability to Peloton, who fixed the bug in software version "PTX14A-290" to no longer allows the use of the 'boot' command on their systems.
It's a Peloton! So what?
You may be wondering what the big deal is about a vulnerability in a Peloton as it is not a device where sensitive data is stored or where you log in to your bank and email accounts.
Hotels, cruise ships, gyms, and vacation rentals are more commonly starting to offer Peloton bikes and treadmills for their guests to use while visiting.
If a threat actor can compromise one of these devices, they could potentially install malware that harvests the accounts of people who use the devices.
The threat actors can then use those accounts to try and compromise other sites with the same credentials.
It is also important to remember that Pelotons are considered infrastructure by houses and commercial locations and may sit on the internal network rather than a more walled-off guest network.
A compromised Peloton would not show any outward signs of tampering but, once hacked by a threat actor, could be used to provide remote access to the network without anyone being the wiser.
Finally, and a bit more concerning, once threat actors gain elevated privileges on the device, they can remotely turn on a camera or microphone.
While it is improbable that Peloton devices would be compromised using this vulnerability and physical access was required, the video below illustrates how McAfee was able to easily load the modified boot image on a Peloton Bike+.



Comments
the_moss_666 - 2 years ago
"While it is improbable that Peloton devices would be compromised using this vulnerability and physical access was required ..."
I woudn't be that optimistic, targeted supply chain attack is always a possibility. This device looks innocent enough to be a good trojan horse.