
A hacking group tracked as MirrorFace has been targeting Japanese politicians for weeks before the House of Councilors election in July 2022, using a previously undocumented credentials stealer named ‘MirrorStealer.’
The campaign was discovered by ESET, whose analysts report they could piece together evidence thanks to operational mistakes made by the hackers that left traces behind.
The hackers deployed the new information-stealing malware along with the group’s signature backdoor, LODEINFO, which communicated with a C2 server known to belong to APT10 infrastructure.
An October 2022 report by Kaspersky described an extensive deployment of LODEINFO against high-profile Japanese targets and highlighted the constant development that goes into improving the custom backdoor.
Spearphishing attacks
The MirrorFace hacking group (APT10 and Cicada) began sending spear-phishing emails to their targets on June 29, 2022, pretending to be PR agents from the recipient’s political party, asking them to post the attached video files on social media.
.png)
In other cases, the threat actors impersonated a Japanese ministry, attaching decoy documents that extract WinRAR archives in the background.
The archive contained an encrypted copy of the LODEINFO malware, a malicious DLL loader, and an innocuous application (K7Security Suite) used for DLL search order hijacking.
This is the same stealthy attack chain that Kaspersky described in its previous report, which loads the backdoor directly in memory.
MirrorStealer operations
APT10 used LODEINFO to deploy MirrorStealer (‘31558_n.dll’) on compromised systems.
MirrorStealer targets credentials stored in web browsers and email clients, including ‘Becky!,’ an email client popular in Japan.
This indicates that MirrorStealer might have been developed explicitly for APT10’s Japan-focused operations.
All stolen credentials are stored in a txt file in the TEMP directory and then wait for LODEINFO to send them to the C2, as MirrorStealer does not support data exfiltration on its own.
LODEINFO is also used as a connecting bridge between the C2 and MirrorStealer, to convey commands to the info-stealer
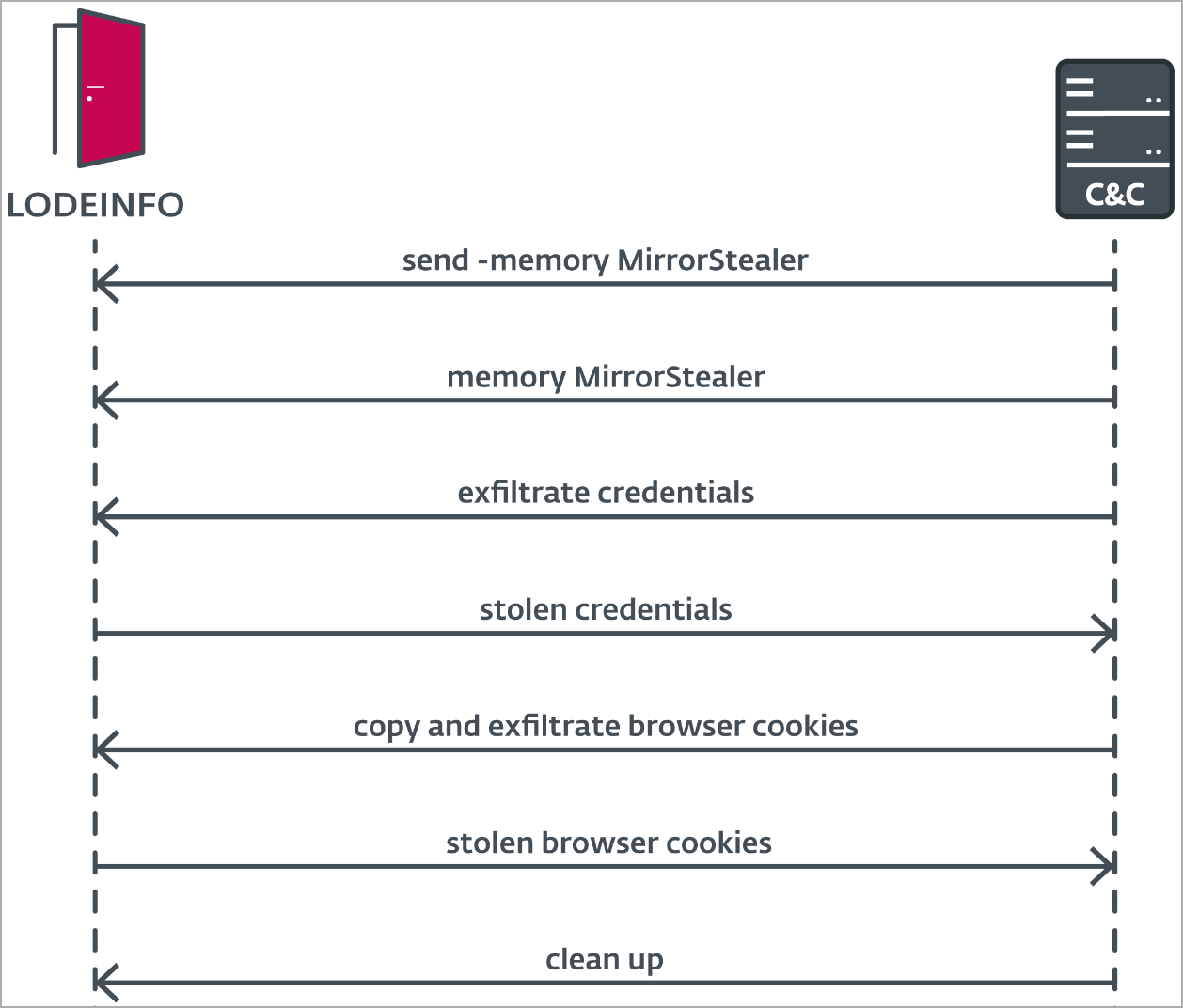
ESET’s analysts observed LODEINFO conveying commands to load MirrorStealer on the memory of the breached system, injecting it into a newly spawned cmd.exe process and running it.
Moreover, there are signs that the remote operator attempted to exfiltrate browser cookies using MirrorStealer, but reverted to using LODEINFO for this action, as the new info-stealer does not support this function.
Leaving traces
APT10 wasn’t very careful in this campaign, failing to remove all traces of its activity on the breached computers and leaving MirrorStealer’s text file containing the collected credentials behind.
Additionally, ESET’s analysts noticed that the hackers issued commands with typos to LODEINFO in several cases, indicating that the technical aspect of the operation is more manual than expected from an APT group.



Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now