
WooCommerce, the popular e-commerce plugin for the WordPress content management system has been updated to patch a serious vulnerability that could be exploited without authentication.
Administrators are urged to install the latest release of the platform as the flaw affects more than 90 versions starting with 5.5.0.
Owned by Automattic, the company behind the WordPress.com blogging service, the WooCommerce plugin has more than five million installations.
Improper sanitization
In a post today, the WooCommerce team says that the bug is critical and it also affects the WooCommerce Blocks plugin for showing products on posts and pages.
Both plugins received an update to version 5.5.1. The fix has been rolling out to affected versions (WooCommerce 3.3 through 5.5 and WooCommerce Blocks 2.5 through 5.5).
The vulnerability has yet to receive a tracking number but its severity score has been calculated at 8.2 out of 10 by Patchstack, a company that protects WordPress sites from plugin vulnerabilities.
Oliver Sild, the founder and CEO of Patchstack, provides some technical details about the bug after noting that the patch eliminates the flaw by modifying two PHP files that allowed injecting malicious code in SQL statements without the need to authenticate.
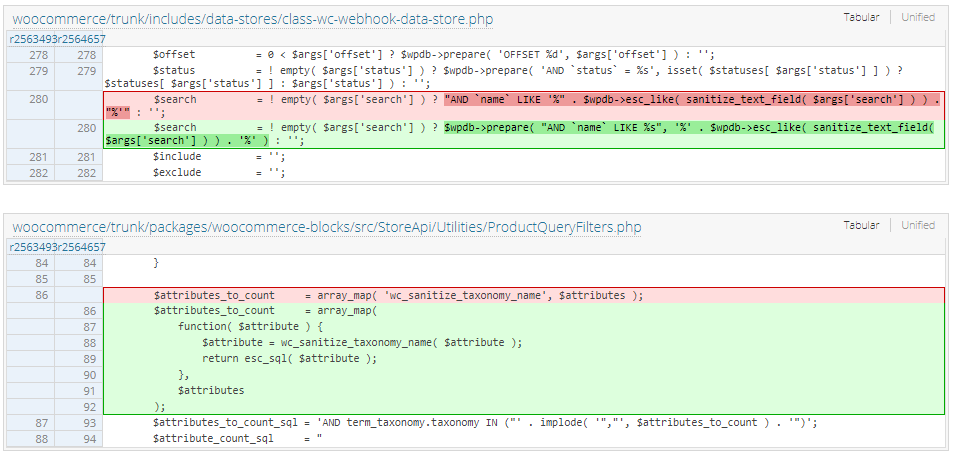
The injection was possible because of “a webhook search function that injected the search parameter into a SQL query without using a prepared statement.”
Sild explains that despite the use of the sanitize_text_field and esc_like functions, the latter could be used without a prepared statement, which no longer happens in version 5.5.1.
As for the lack of authentication, the researcher says that it was due to the improper escape of the $attributes parameter in a public-facing endpoint that did not require authentication.
“The $attributes parameter in this endpoint (line 86) is taken from the user input and then processed and injected into a SQL query that was not properly escaped,” Sild says.
The researcher clarified further saying that “the only sanitization against this parameter was the sanitize_title function (through wc_sanitize_taxonomy_name). However, this does not provide sufficient protection.”
Exploitation risk
Affected WooCommerce installations are currently receiving the patch automatically with the help of the WordPress.org Plugin Team. Sites on the WordPress.com blogging platform have already received the fix.
At the same time, the WooCommerce team sent out an email informing users about the vulnerability and that applying it is a critical precaution.
An attacker taking advantage of this SQL injection flaw could obtain store-related information, administrative details, and data about orders and customers.
Patchstack has not seen any attempts to exploit this vulnerability in the wild but threat actors may jump at the occasion before the fix reaches more sites.
WooCommerce strongly recommends updating to the latest version followed by changing the passwords.
The developers learned about the bug after a security researcher named Josh reported it through Automattic's bug bounty program on HackerOne. As per the rewards info for the program and given that WooCommerce marked the flaw as critical, the researcher stands to get a $500 bounty.
Update [July 16, 2021]: The vulnerability is being exploited in the wild. Wordfence has seen "extremely limited evidence" of hacking attempts, suggesting that the attacks are highly targeted. Looking at the data, the researchers saw that attacks originated from four IP addresses:
107.173.148.66
84.17.37.76
122.161.49.71
The number of attacks is expected to increase when an exploit becomes wider available (proof-of-concept code already exists but access is limited).



Comments
PluginVulns - 2 years ago
Severity scores don't appear to be a meaningful metric. For example, the company you cite providing one, Patchstack, earlier this year gave a "vulnerability" that required the attacker to be logged in to WordPress as an Administrator a score of 7.2 out of 10: https://www.pluginvulnerabilities.com/2021/06/24/the-wp-super-cache-vulnerability-that-wasnt-a-vulnerability/
joshwenke - 2 years ago
SQL injection is easily preventable with prepared statements. An oversight like this is a reason NOT to choose WooCommerce.