
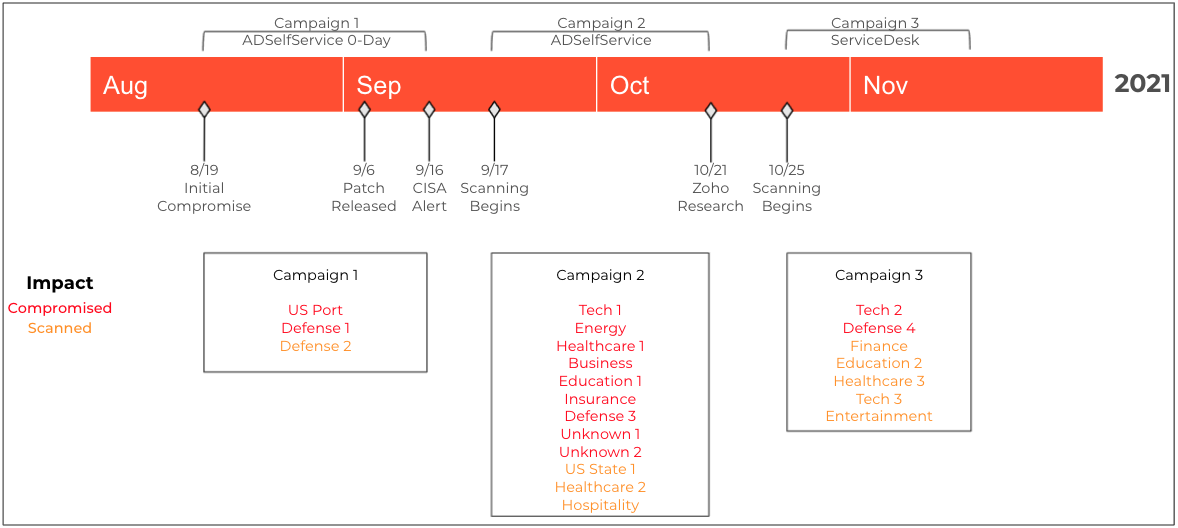
An advanced persistent threat (APT) group that had been exploiting a flaw in the Zoho ManageEngine ADSelfService Plus software has pivoted to leveraging a different vulnerability in another Zoho product.
The actor has been seen exploiting an unauthenticated remote code execution issue in Zoho ServiceDesk Plus versions 11305 and older, currently tracked as CVE-2021-44077.
Source: Unit42
Zoho addressed the RCE flaw on September 16, 2021, and on November 22, 2021, the company published a security advisory to alert customers of active exploitation. Users were slow to update, though, and remained vulnerable to attacks.
According to a report from Palo Alto Networks’ Unit42, there is no public proof-of-concept exploit for CVE-2021-44077, which suggests that the APT group leveraging it developed the exploit code itself and are using it exclusively for now.
Exploiting the RCE to drop the ‘Godzilla’ webshell
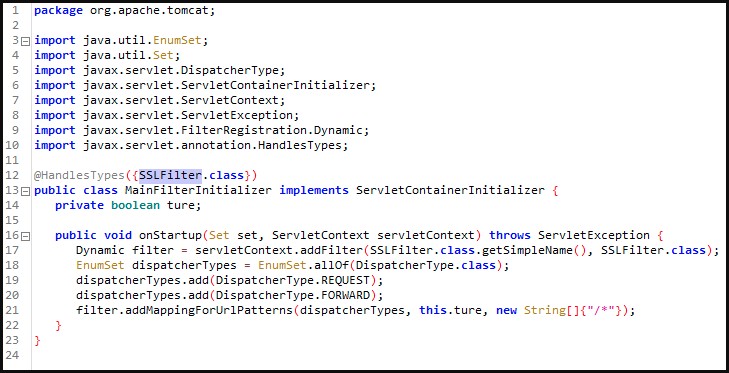
The actors exploit the flaw by sending two requests to the REST API, one to upload an executable (msiexec.exe) and one to launch the payload.
This process is done remotely and requires no authentication to the vulnerable ServiceDesk server.
When ServiceDesk executes the payload, a mutex is created and a hardcoded Java module is written to “../lib/tomcat/tomcat-postgres.jar,” a variant of the ‘Godzilla’ webshell that is loaded into ServiceDesk after killing ‘java.exe’ and restarting the process.
According to the researchers, the actor used the same webshell secret key seen in the ADSelfService Plus campaign, but this time it installs as an Apache Tomcat Java Servlet Filter.
Source: Unit42
“The fact that this Godzilla webshell is installed as a filter means that there is no specific URL that the actor will send their requests to when interacting with the webshell and the Godzilla webshell filter can also bypass a security filter that is present in ServiceDesk Plus to stop access to webshell files” – reads Unit42’s analysis
“It appears that the threat actor leveraged publicly available code called tomcat-backdoor to build the filter and then added a modified Godzilla webshell to it,” the researchers note.
Palo Alto Networks has seen evidence that may connect these attacks to the Chinese APT27 group (Emissary Panda), who have previously deployed Godzilla against high-profile targets, but the clues are insufficient for clear attribution.
Organizations are strongly recommended to patch their Zoho software as soon as possible and review all files created in ServiceDesk Plus directories since early October 2021.
Source: Unit42
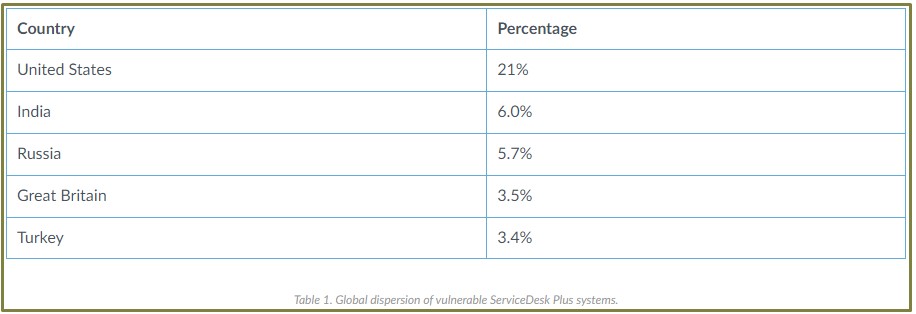
At this time, network scans reveal over 600 vulnerable systems in the United States and another 2,100 in India, Russia, Great Britain, Turkey, and others.
Many of those vulnerable deployments are found in government systems, universities, healthcare organizations, and other critical entities.
Update Dec 03: CISA published an alert on the exploitation of CVE-2021-44077, sharing a long list of novel IoCs which could help defenders detect and mitigate the threat.



Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now