
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is currently detecting at least two Chrome updates as malware, tagging the Slovenian localization file bundled with the Google Chrome installer as a malicious file.
System admins are reporting that Microsoft's enterprise endpoint security platform (previously known as Microsoft Defender ATP) is detecting the sl.pak component in both Chrome 88.0.4324.104 and 88.0.4324.146 (the latest version, released yesterday) installers as a PHP/Funvalget.A backdoor.
Even though multiple Microsoft security accounts were tagged on Twitter and the company was also contacted to provide a statement regarding this ongoing issue, Redmond hasn't yet provided an official reply.
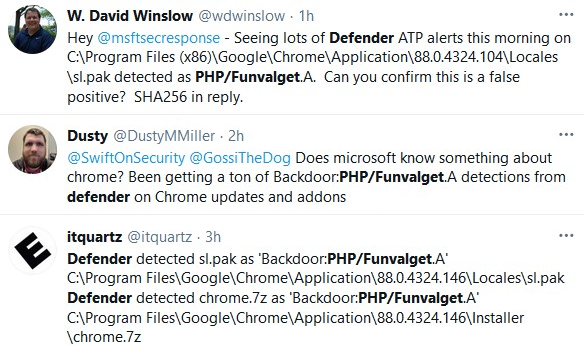
BleepingComputer has also contacted Microsoft for more information and to confirm that this is an issue of a false positive detection but has not heard back.
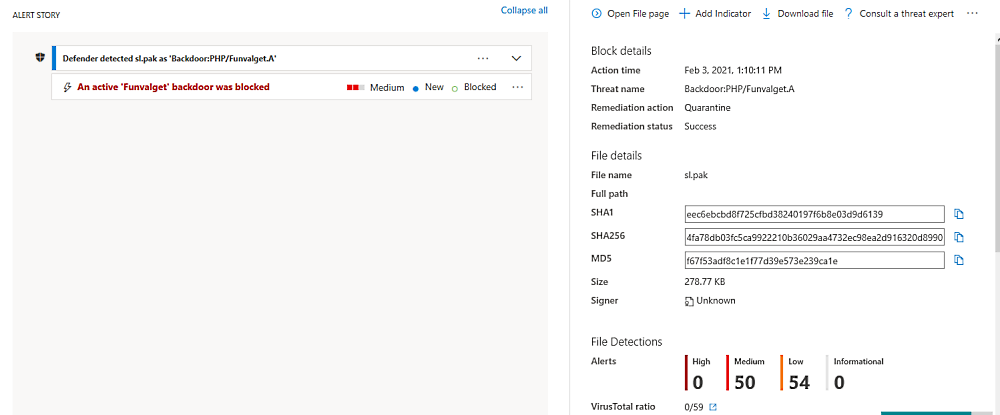
As first reported by ZDNet, according to a screenshot showing the Chrome sl.pak language file being tagged as a backdoor, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint automatically blocks the detected files using quarantine as a remediation action.
Microsoft has stated that the issue was an automation error and is now resolved.
"We’ve corrected an automation error that incorrectly classified the installation package as malware.” – a Microsoft spokesperson.
To clear the cached detection on endpoints in their environment, systems admins are advised to update to the latest malware definitions by using this procedure:
- Go into Defender's directory using a command prompt opened as admin:
cd %ProgramFiles%\Windows Defender - Run these two commands to clear the current cache and trigger an update:
MpCmdRun.exe -removedefinitions -dynamicsignaturesandMpCmdRun.exe -SignatureUpdate



Comments
UberGeekDude - 3 years ago
Conspiracy Theory: This sounds just like another Microsoft ploy to get more people using Edge browser. Tell people their Chrome installation is a backdoor to encourage them to switch.
NoneRain - 3 years ago
Nah... this is relatively common to happen with all AV. Also, only happening with ATP...