
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) has added two more vulnerabilities to its list of actively exploited bugs, a code injection bug in the Spring Cloud Gateway library and a command injection flaw in Zyxel firmware for business firewalls and VPN devices.
The Spring Framework vulnerability (CVE-2022-22947) is a maximum severity weakness that attackers can abuse to gain remote code execution on unpatched hosts.
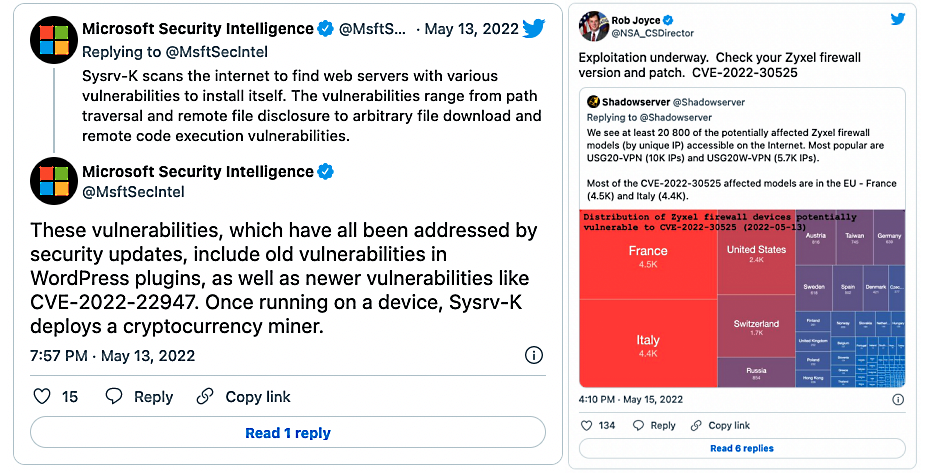
This critical bug is currently being exploited by a botnet known as Sysrv to install cryptomining malware on vulnerable Windows and Linux servers.
Threat actors are also abusing a critical Zyxel firmware vulnerability (CVE-2022-30525), patched on April 28, 2022 (without public disclosure) and under active exploitation starting May 13th (one day after Zyxel finally issued a security advisory).
Rapid7 found over 15,000 vulnerable Zyxel products exposed to Internet access, while the Shadowserver Foundation spotted at least 20,000 potentially impacted devices.
Since exploitation began, NSA Cybersecurity Director Rob Joyce also warned admins about ongoing exploitation and encouraged them to update their Zyxel firewalls' firmware if vulnerable.
Federal agencies have three weeks to patch
According to a November binding operational directive (BOD 22-01) issued by CISA to reduce the risk of known exploited bugs across US federal networks, all Federal Civilian Executive Branch Agencies (FCEB) agencies must patch their systems against bugs added to the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog (KEV).
The US cybersecurity agency gave them three weeks to fix these flaws until June 6th to block ongoing exploitation attempts.
Although the BOD 22-01 directive only applies to US FCEB agencies, CISA also strongly urged all US organizations from the private and public sectors to prioritize patching these actively exploited bugs.
Following the agency's advice should notably reduce the attack surface threat actors can exploit in attempts to breach vulnerable networks.
Last week, CISA also added an actively exploited Windows LSA spoofing zero-day (CVE-2022-26925), now confirmed as a new PetitPotam Windows NTLM Relay attack vector.
However, this Windows security flaw was removed from the KEV catalog after it was discovered that Microsoft's May 2022 Patch Tuesday updates are triggering Active Directory (AD) authentication issues on domain controllers.
Update: Corrected Zyxel patching timeline.


Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now