How Did Authorities Identify the Alleged Lockbit Boss?
Krebs on Security
MAY 13, 2024
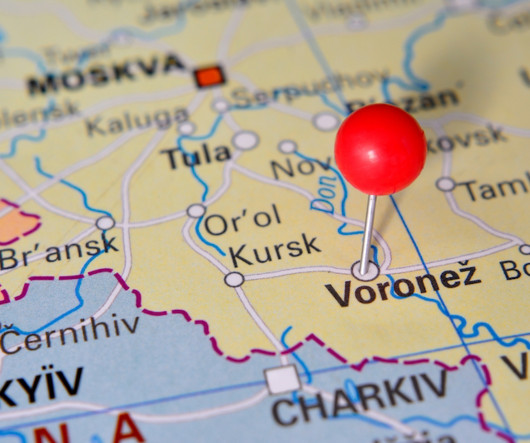
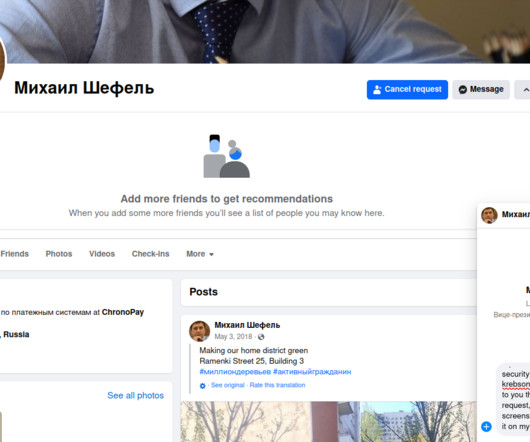
and Australia in sanctioning and charging a Russian man named Dmitry Yuryevich Khoroshev as the leader of the infamous LockBit ransomware group. According to Constella, this email address was used in 2010 to register an account for a Dmitry Yurievich Khoroshev from Voronezh, Russia at the hosting provider firstvds.ru.










Let's personalize your content