Discover 2022’s Nastiest Malware
Webroot
OCTOBER 14, 2022
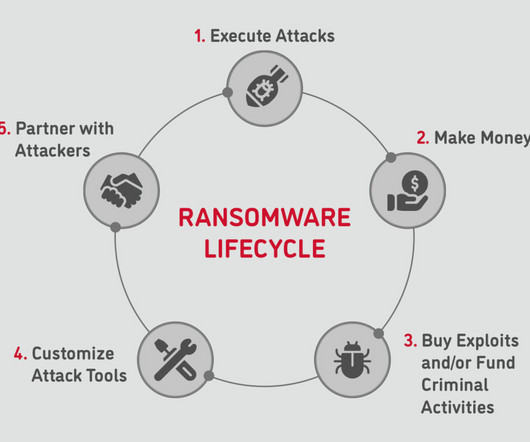
Since the mainstreaming of ransomware payloads and the adoption of cryptocurrencies that facilitate untraceable payments, malicious actors have been innovating new methods and tactics to evade the latest defenses. In other words, 2022 has been an eventful year in the threat landscape, with malware continuing to take center stage.













Let's personalize your content