Video: How Hackers Steal Your Cookies & How to Stop Them
eSecurity Planet
NOVEMBER 6, 2024
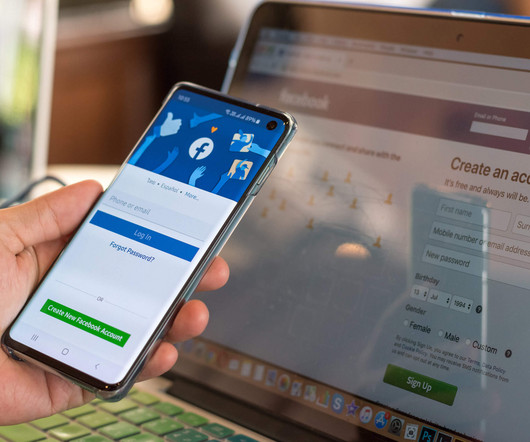
Attackers can steal your cookies through phishing, malware, and MITM attacks, leading to data theft, financial loss, and identity theft. Initial Attack Vector Attackers might send phishing emails or create fake websites. Though cookies themselves don’t steal passwords, they can be hijacked to access sensitive data.

















Let's personalize your content