How to Prevent DNS Attacks: DNS Security Best Practices
eSecurity Planet
DECEMBER 8, 2023
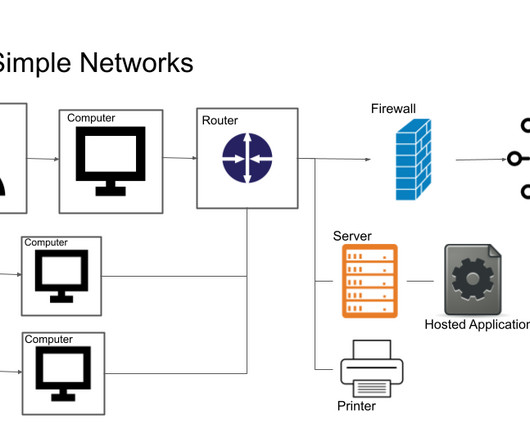
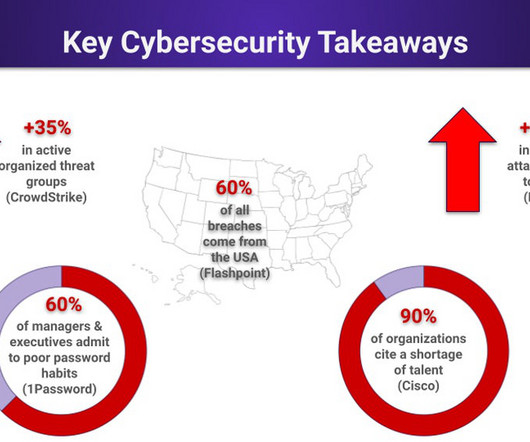
Domain name service (DNS) attacks threaten every internet connection because they can deny, intercept, and hijack connections. With the internet playing an increasing role in business, securing DNS plays a critical role in both operations and security. TLS and HTTPS inherently create secured and encrypted sessions for communication.











Let's personalize your content