Glove Stealer bypasses Chrome’s App-Bound Encryption to steal cookies
Security Affairs
NOVEMBER 15, 2024
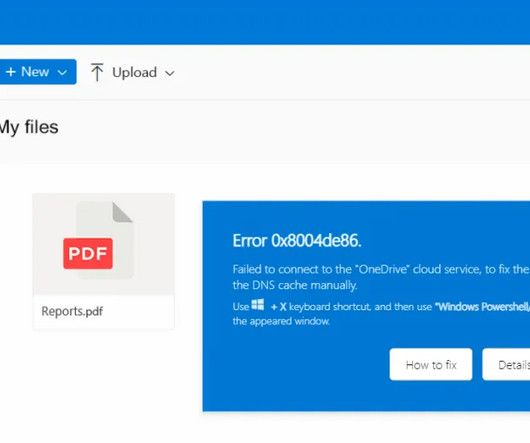
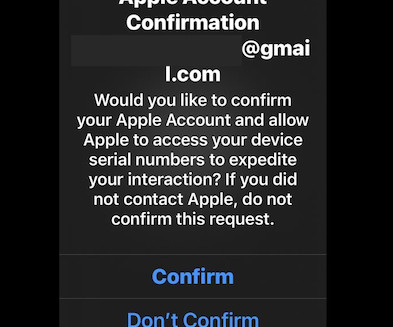
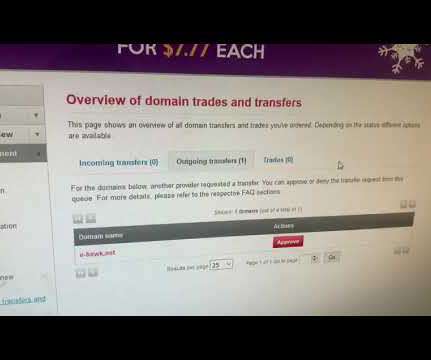
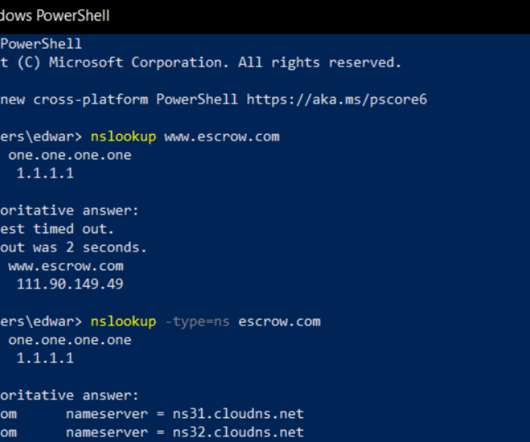
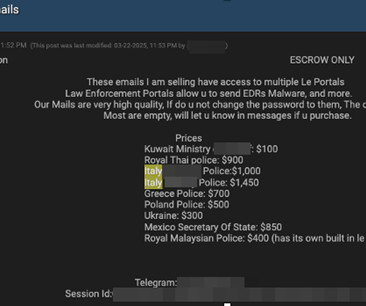
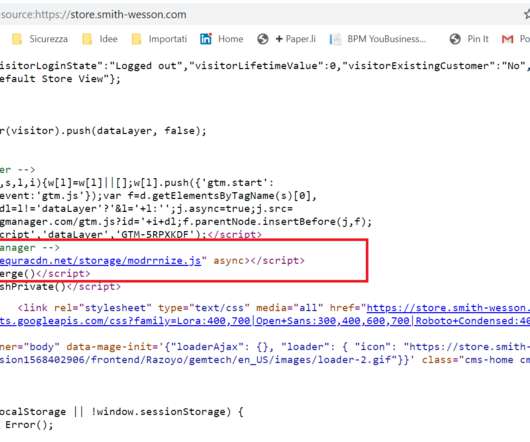
The Glove Stealer malware exploits a new technique to bypass Chrome’s App-Bound encryption and steal browser cookies. The malware could harvest a huge trove of data from infected systems, including cookies, autofill, cryptocurrency wallets, 2FA authenticators, password managers, and email client information.












































Let's personalize your content