SharkBot, a new Android Trojan targets banks in Europe
Security Affairs
NOVEMBER 15, 2021
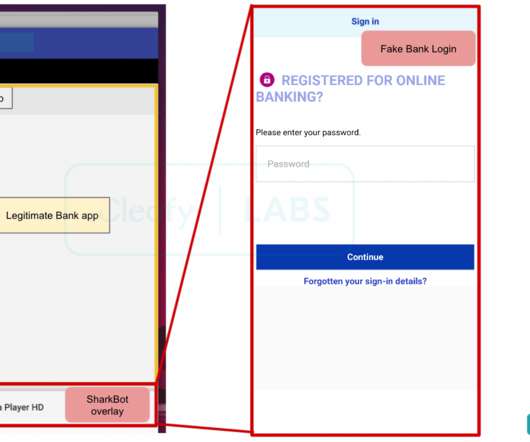
The trojan allows to hijack users’ mobile devices and steal funds from online banking and cryptocurrency accounts. At the time of writing, SharkBot appears to have a very low detection rate by antivirus solutions since. login credentials, personal information, current balance, etc.). ” concludes the report.
















Let's personalize your content