Reading INTERPOL the African Cyberthreat Assessment Report 2021
Security Affairs
OCTOBER 30, 2021
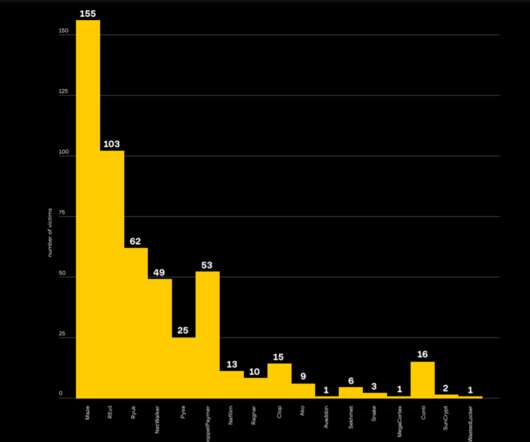
INTERPOL published the African Cyberthreat Assessment Report 2021, a report that analyzes evolution of cybercrime in Africa. A new report published by INTERPOL, titled the African Cyberthreat Assessment Report 2021 , sheds the light on cybercrime in Africa. of the overall number.

























Let's personalize your content