3 ways DNS filtering can save SMBs from cyberattacks
Malwarebytes
JUNE 1, 2022
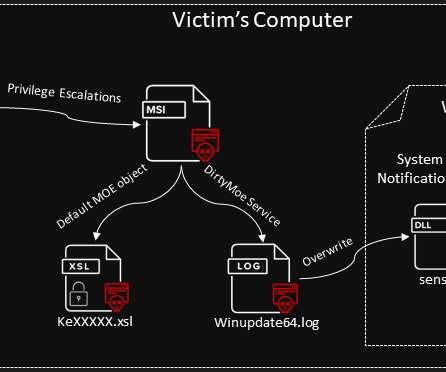
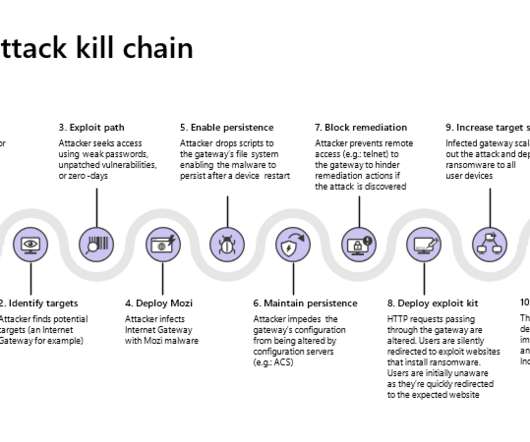
That’s where DNS filtering comes in. But first, DNS in a nutshell. So normally, every time your customer types in your web address, their computer makes a request to a DNS server. The DNS server, in turn, tells the computer where to go. But which web-based cyberthreats in particular does DNS filtering stop, you ask?






























Let's personalize your content