Why Malware Crypting Services Deserve More Scrutiny
Krebs on Security
JUNE 21, 2023
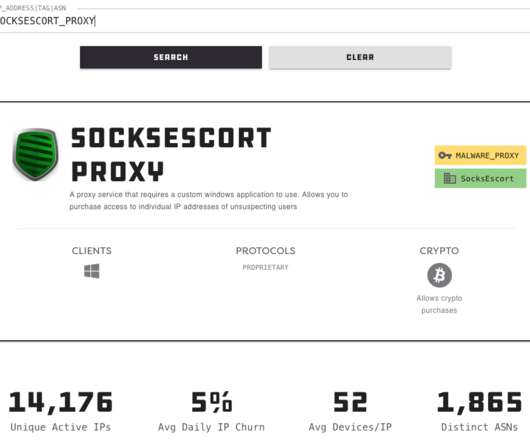
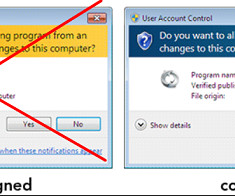
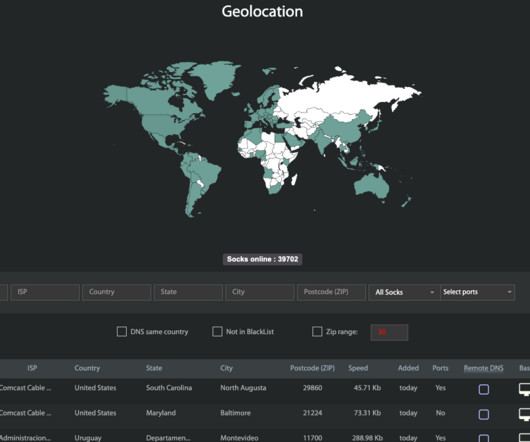
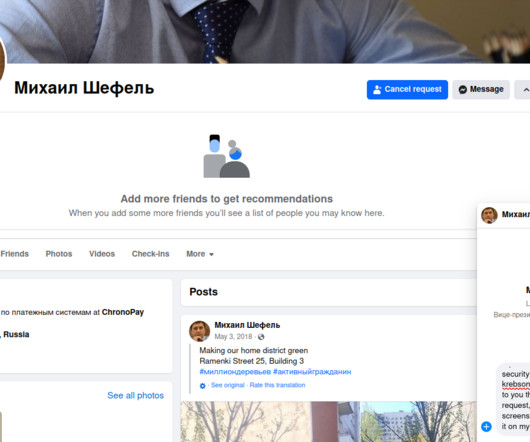
If you operate a cybercrime business that relies on disseminating malicious software, you probably also spend a good deal of time trying to disguise or “crypt” your malware so that it appears benign to antivirus and security products. This story explores the history and identity behind Cryptor[.]biz WHO RUNS CRYPTOR[.]BIZ?
























Let's personalize your content