Profiling Russia’s U.S Election Interference 2016 – An OSINT Analysis
Security Boulevard
JANUARY 26, 2022
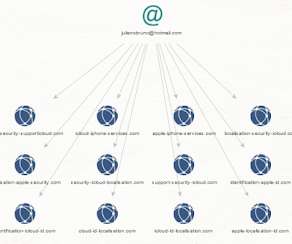
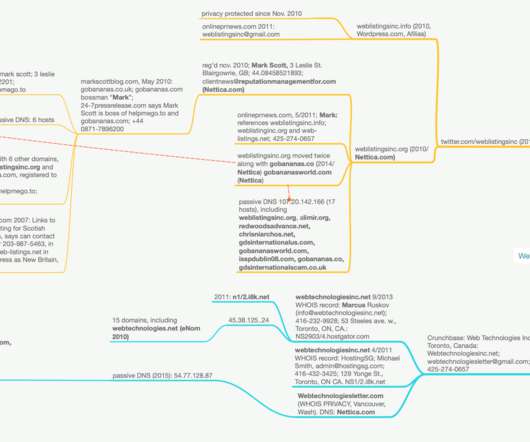
In this analysis we’ll take a closer look at the Internet connected infrastructure behind the U.S Election 2016 campaign in terms of malicious activity and offer practical and relevant including actionable threat intelligence on their whereabouts. Elections 2016 campaign: linuxkrnl[.]net. accounts-qooqle[.]com.
































Let's personalize your content