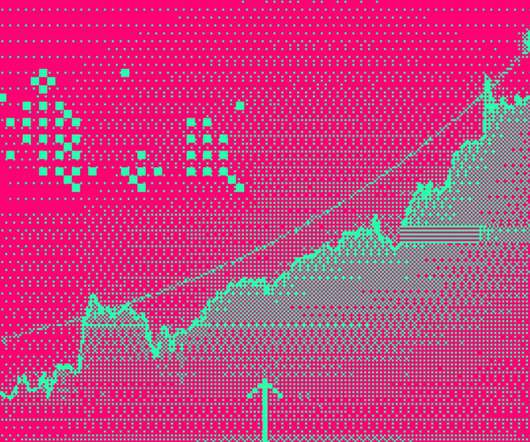
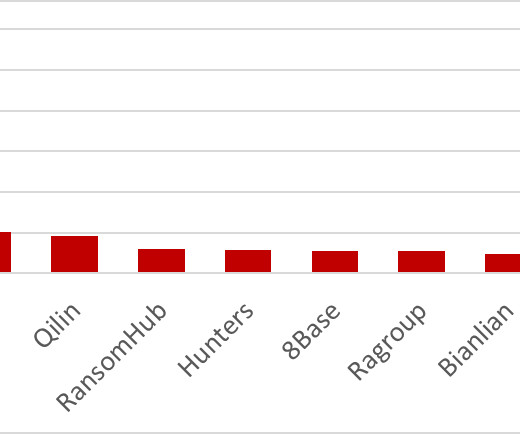
Known ransomware attacks up 68% in 2023
Malwarebytes
FEBRUARY 6, 2024
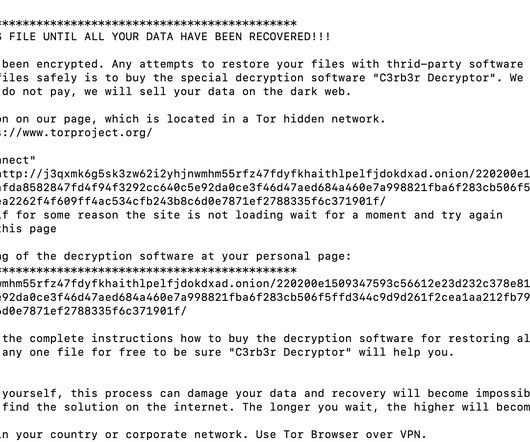
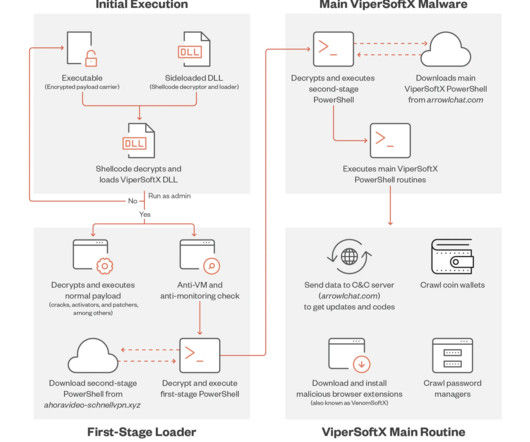
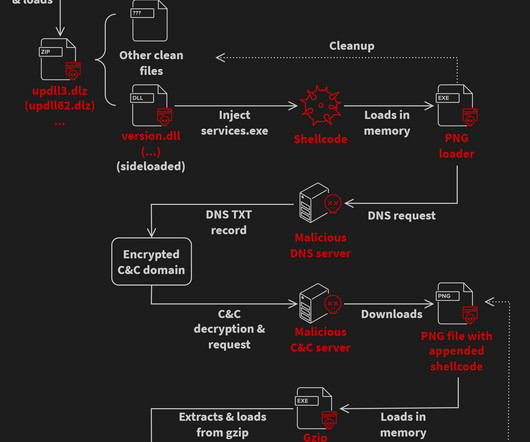
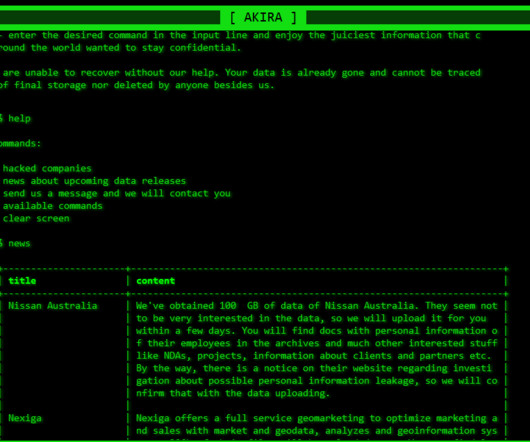
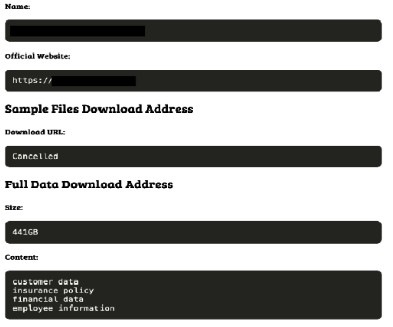
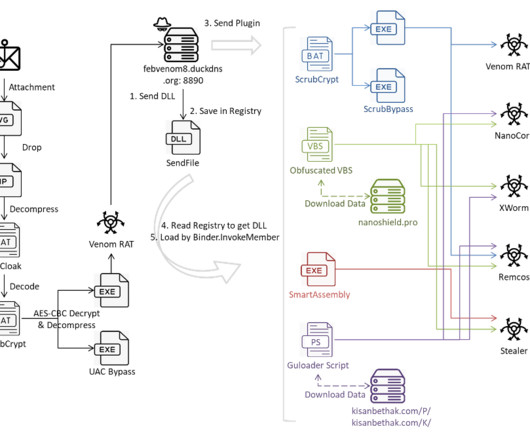
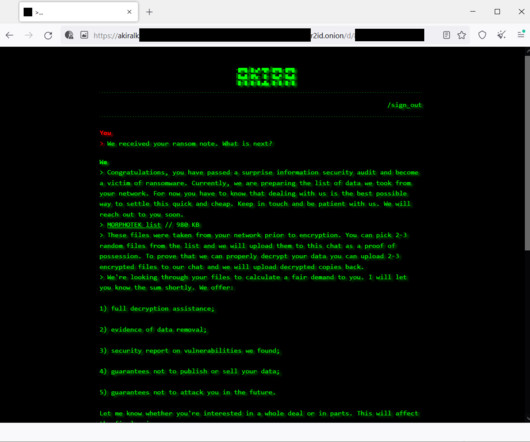
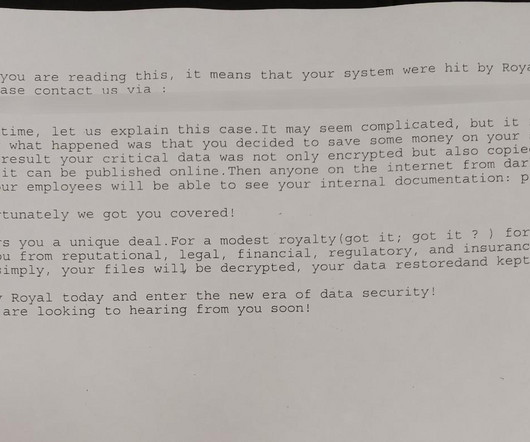
Today, Malwarebytes released its 2024 State of Malware report, detailing six cyberthreats that resource-constrained IT teams should pay attention to in 2024. Big game attacks extort vast ransoms from organizations by holding their data hostage—either with encryption, the threat of damaging data leaks, or both.


































Let's personalize your content