China-linked threat actors compromised multiple telecos and spied on a limited number of U.S. government officials
Security Affairs
NOVEMBER 14, 2024
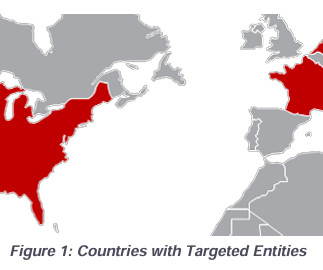
government officials. telecoms, compromising networks to steal call records and access private communications, mainly of government and political figures. broadband providers, including Verizon, AT&T, and Lumen Technologies, potentially accessing systems for lawful wiretapping and other data. .” broadband providers.















































Let's personalize your content