What Is DNS Security? Everything You Need to Know
eSecurity Planet
NOVEMBER 10, 2023
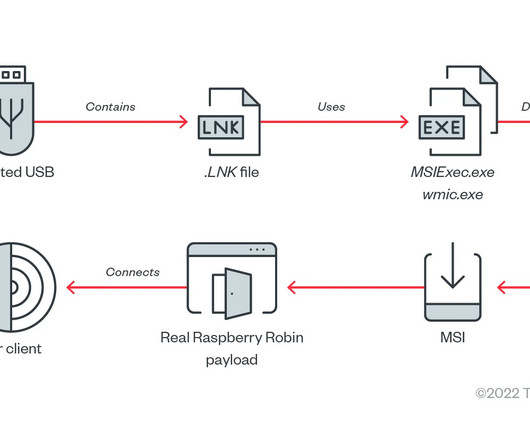
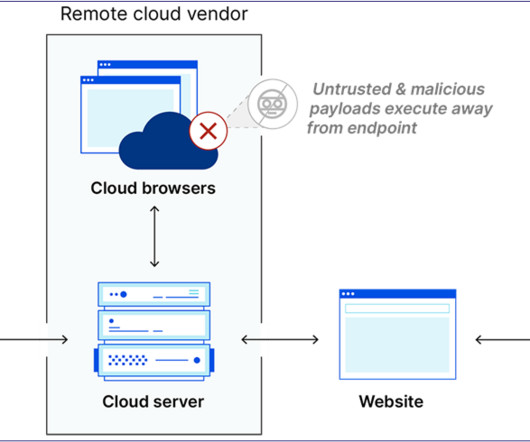
DNS security protects the domain name system (DNS) from attackers seeking to reroute traffic to malicious sites. Since a majority of business IT traffic now accesses or passes through the internet, DNS plays an increasingly important — and vulnerable — role. in the DNS cache for more efficient delivery of information to users.









































Let's personalize your content